Finding the right PBT resin for precision molding in China can derail your entire project timeline. Many engineers struggle with inconsistent material supply, unclear grade specifications, and processing challenges that lead to costly trial-and-error cycles.
Valox PBT offers superior dimensional stability and moisture resistance compared to nylon alternatives, making it the preferred choice for automotive connectors and electrical components requiring reliable performance in harsh environments.

Through my work at MTM, I’ve helped engineering teams navigate the complexities of Valox grade selection and processing optimization. This guide covers everything from material properties to molding parameters, ensuring you make informed decisions for your next project in China.
Strategic Importance Of Valox PBT In Precision Engineering
When precision is non-negotiable, material choice becomes critical. In engineering, we often weigh options like Nylon, PET, and Valox PBT. While each has its merits, Valox resin consistently provides superior dimensional stability, especially in environments with fluctuating humidity and temperature.
Why Valox PBT Stands Out
Nylon’s tendency to absorb moisture can lead to swelling and property changes, a risk for tight-tolerance parts. Valox PBT, however, exhibits very low moisture absorption. This ensures components maintain their specified dimensions and performance over their entire service life.
Comparative Stability
The data clearly shows why Valox is often preferred for high-precision applications.
| Material | Moisture Absorption (at 23°C, 50% RH) | Impact on Dimensional Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Valox PBT | Very Low (<0.2%) | High |
| Nylon (PA66) | Moderate (~2.5%) | Low to Moderate |
| PET | Low (<0.6%) | Moderate to High |
This stability makes Valox a reliable choice for complex engineering designs.
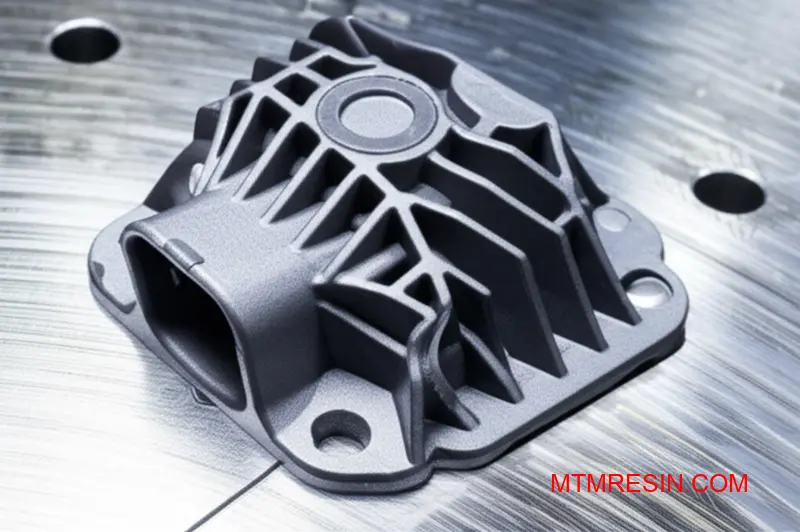

Beyond Dimensional Stability
Valox resin’s benefits extend past stability. Its excellent electrical insulation properties make it a top choice for automotive connectors and electronic housings. These applications demand consistent performance where even minor material changes from moisture absorption can cause critical failures over time.
Furthermore, its resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including automotive fluids and industrial solvents, is a significant advantage. This ensures long-term reliability in aggressive operational environments, a key factor for components used in industrial or automotive settings.
Processing Considerations for Mold Trials
Achieving these properties depends on correct processing. Valox PBT is sensitive to Hydrolysis1 during molding if the pellets are not properly dried beforehand. This chemical process can degrade the polymer chain, significantly weakening the final part’s mechanical strength and integrity.
At MTM, we ensure our Valox trial materials are stored in optimal conditions. This prevents such issues, allowing your team in China to conduct accurate mold trials without worrying about material quality compromising the results.
| Parameter | Valox PBT | Nylon (PA66) |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Temperature | 120-140°C | 80-90°C |
| Drying Time | 2-4 hours | 2-4 hours |
| Melt Temperature | 240-260°C | 260-290°C |
| Mold Temperature | 60-90°C | 80-120°C |
In summary, Valox PBT offers exceptional dimensional stability and chemical resistance crucial for precision components. Proper material handling is key to unlocking its full potential, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications from electronics to automotive parts.
Deciphering The Valox Resin Portfolio: From 310 To 420SEO
Navigating the Valox resin portfolio can be complex. Each grade offers distinct properties tailored for specific applications. Understanding the core differences between the series is the first step toward making an informed material selection for your project. This is especially true for demanding industries.
The Core Valox Families
The portfolio is primarily divided into unfilled and reinforced grades. The 300 series represents the unfilled PBT resins, known for their excellent processability and surface finish. In contrast, the 400 series incorporates glass fiber reinforcement, significantly enhancing mechanical properties.
Key Series Comparison
| Series | Key Feature | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 300 Series | Unfilled PBT | Excellent surface aesthetics and flow |
| 400 Series | Glass-Reinforced PBT | High strength and stiffness |
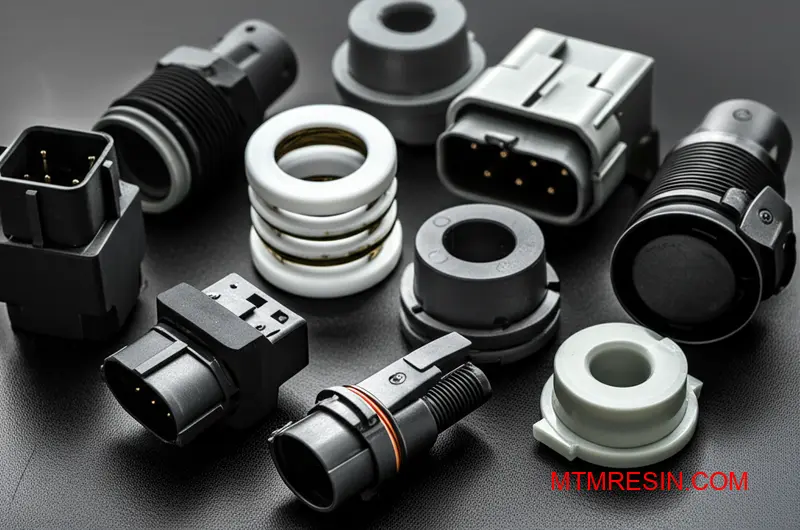

The main distinction within the Valox family lies between its unfilled and reinforced grades. This choice directly impacts the final part’s performance characteristics. It’s a frequent topic of discussion when clients need materials for mold trials in China.
300 Series vs. 400 Series
The 300 series, being unfilled, is ideal for parts requiring a high-quality surface finish and intricate details. Think electrical connectors or appliance housings. Its excellent flow properties make it suitable for complex mold geometries.
The 400 series is the workhorse for structural components. Adding glass fibers creates a composite with superior strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability. This makes it a go-to choice for automotive parts, industrial pump housings, and load-bearing brackets where mechanical integrity is non-negotiable.
Specific Grade Applications
Valox 357
Valox 357 is an impact-modified, unfilled grade. We’ve seen it used extensively in applications requiring good chemical resistance and enhanced toughness over standard PBT, such as in certain automotive sensor housings.
Valox 420SEO
Valox 420SEO is perhaps the most recognized grade. It’s a 30% glass-filled PBT with a V-0 flame rating. Its balance of high strength, stiffness, and electrical properties makes it a staple for connectors, bobbins, and switches. Its excellent Creep Resistance2 is critical here.
Valox 553
Valox 553 is a 30% glass/mineral reinforced resin. This blend offers very low warpage and excellent dimensional stability, a common requirement for large, flat automotive body panels or intricate electronic enclosures where flatness is key.
Understanding the Valox portfolio is crucial for material selection. The unfilled 300 series excels in aesthetics, while the reinforced 400 series provides structural strength. Grades like 420SEO and 553 offer specialized properties for demanding electrical and automotive applications.
Key Physical Properties: Why Engineers Specify Valox PBT
The Engineering Advantage
Engineers often choose Valox PBT for its consistent performance. It’s a reliable material that balances mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and processability. This makes it a go-to choice for complex components where failure is not an option. Predictable results are essential.
Balancing Performance and Reliability
When specifying materials, balancing multiple requirements is key. Valox excels here. Its unique combination of properties ensures that parts not only meet initial specs but also maintain their integrity over the product’s lifespan, which is crucial for brand reputation and safety.
| Property Focus | Typical Application | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Housings, Connectors | Durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Automotive Parts | Longevity |
| Electrical Insulation | Switches, Sockets | Safety |
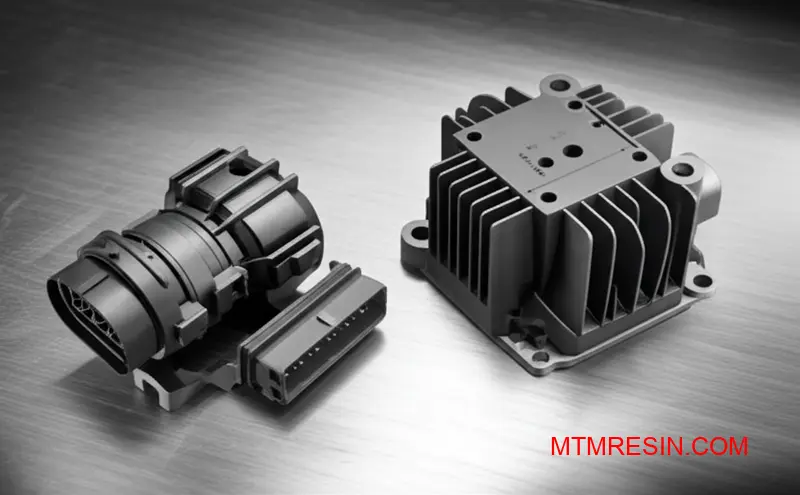

Core Performance Attributes
Valox PBT’s value is clear when examining its specific resistances. In the automotive world, its excellent Valox chemical resistance is a major advantage. Components exposed to oils, greases, and various fuels maintain structural integrity, preventing swelling or cracking throughout the vehicle’s service life.
Electrical Insulation Properties
For electrical applications, the focus shifts to insulation. Valox provides a high dielectric strength3, crucial for preventing electrical current leakage. Its stable dielectric constant PBT also benefits high-frequency components, ensuring signal integrity in modern electronics. This is essential for safety and performance.
Stability Under Heat
Heat is another critical factor. The high heat deflection temperature of Valox grades ensures components don’t warp when exposed to high temperatures. This is vital for under-the-hood automotive parts or inside compact, hot-running electronic devices, where performance must remain stable.
| Property | Automotive Sector Relevance | Electrical Sector Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands oils, fuels, solvents | Resists cleaning agents, industrial chemicals |
| Dielectric Strength | Insulates sensors and connectors | Prevents arcing in switches, sockets |
| Heat Resistance | Maintains integrity near engines | Handles heat from high-power components |
Valox PBT is specified by engineers for its robust physical properties. Its superior chemical resistance, high dielectric strength, and excellent heat stability make it a reliable choice for critical components in the demanding automotive and electrical industries, ensuring long-term performance and safety.
Unfilled Vs. Glass-Filled Valox: Impact On Structural Integrity
Choosing between unfilled and glass-filled Valox is a critical decision for structural integrity. The addition of glass fibers dramatically alters the material’s properties. It’s not just about adding strength; it’s a trade-off between stiffness, toughness, and even how the part processes.
Unfilled Valox Resin
Unfilled PBT, or Valox, offers good general-purpose performance. It has excellent chemical resistance and electrical properties. Its structural use is best for components that do not face high mechanical stress but require dimensional stability and a good surface finish.
Glass-Filled Valox Resin
Glass-reinforced Valox significantly boosts mechanical properties. Adding glass fibers increases rigidity and strength, making it suitable for demanding applications. However, this reinforcement can reduce impact strength and introduce processing challenges that must be considered.
Key Performance Comparison
| Property | Unfilled Valox | Glass-Filled Valox |
|---|---|---|
| Stiffness | Moderate | Very High |
| Tensile Strength | Good | Excellent |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Surface Finish | Excellent | Good |
When we move beyond the datasheet, the differences between unfilled vs filled resin become even more clear. Adding glass fibers is not a simple upgrade; it fundamentally changes the material’s behavior. We often advise clients to consider these practical trade-offs during mold trials.
Impact of Glass Reinforcement
Glass-reinforced Valox provides a substantial increase in tensile strength and Flexural Modulus4. This makes it ideal for parts that must resist bending and deformation under load, such as brackets, housings, or connectors. The fibers act as a skeleton within the polymer matrix.
The Brittleness Trade-Off
However, this added stiffness comes at a cost. The fibers can interrupt the polymer chain’s ability to absorb impact energy, leading to a more brittle material. An unfilled Valox part might dent or deform on impact, while a glass-filled version is more likely to crack.
Processing Considerations
Furthermore, the orientation of glass fibers during injection molding can cause anisotropic shrinkage, leading to warpage. This is a common issue we help troubleshoot at MTM, ensuring our clients’ molds are designed to accommodate the unique behavior of glass reinforced Valox. Selecting the correct grade is vital.
Glass-filled Valox provides superior stiffness and tensile strength for load-bearing parts. Unfilled Valox offers better impact resistance and a finer surface finish. The final choice depends on balancing these mechanical trade-offs to meet your specific application’s structural demands.
Flame Retardant Considerations: Understanding Valox V0 Ratings
When designing electronic components, flame retardancy isn’t just a feature; it’s a critical safety requirement. The UL94 V0 rating is the gold standard for many applications. This rating ensures a material will self-extinguish quickly after exposure to a flame, minimizing fire risk.
Why V0 is a Benchmark
Materials like Valox PBT are frequently chosen for their excellent electrical and mechanical properties. Achieving a V0 rating, particularly in thin-walled designs, demonstrates superior formulation. It is essential for parts like connectors and circuit breakers where heat and electrical currents are constant.
Understanding the Ratings
A V0 rating is more stringent than V1 or V2, as it allows for minimal burning and no flaming drips.
| Rating | Burning Time | Dripping |
|---|---|---|
| V0 | Stops within 10s | None allowed |
| V1 | Stops within 30s | None allowed |
| V2 | Stops within 30s | Flaming drips allowed |
This distinction is crucial for material selection during mold trials.
For electronic components, meeting regulatory standards like UL94 is non-negotiable. The challenge intensifies as part designs become smaller and thinner. A material that achieves V0 at 3.0mm might fail at 0.8mm, a common thickness for modern connectors.
The Nuances of UL94 Testing
The UL94 vertical burn test is a rigorous process. A flame is applied to a sample for a set duration, and the time it takes to self-extinguish is measured. This process helps us understand a material’s real-world performance under thermal stress and is a key factor in material validation.
Thin-Wall Performance
Achieving a V0 rating in thin sections is a significant engineering feat. The reduced material mass can burn through more quickly. This is where specific grades of flame retardant PBT, like certain Valox resins, truly shine. They are formulated to maintain flame retardancy even at minimal thicknesses. Another key metric we often consider is the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI)5, which helps quantify flammability.
Recommended Valox Grades for V0
In my work at MTM, I often guide clients toward specific Valox grades based on their application’s wall thickness.
| Valox Grade | V0 Thickness (Typical) | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Valox 420SEO | 0.75 mm | Connectors, Switches |
| Valox DR48 | 1.5 mm | Housings, Sockets |
| Valox 357X | 0.4 mm | Miniature Components |
Choosing the right grade is vital for passing certification and ensuring product reliability.
Selecting the correct Valox grade with a UL94 V0 rating at the required thickness is vital for electronic component safety and compliance. At MTM, we stock these specific flame retardant PBT grades to ensure your mold trials meet these standards.
Valox Vs. Nylon 66: Choosing For Electrical Applications
When selecting a material for electrical applications, especially connectors, the environment plays a huge role. The choice between Valox (PBT) and Nylon 66 (PA66) often comes down to one critical factor: moisture. While both are excellent engineering thermoplastics, their performance in humid conditions differs significantly.
The Challenge of Humid Environments
Nylon 66 is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the air. This absorption can alter its dimensional stability and electrical insulating properties. For a precise connector, this is a major concern. Valox, in contrast, exhibits much lower moisture absorption, making it a more stable choice.
Initial Property Comparison
| Property | Valox (PBT) | Nylon 66 (PA66) |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Absorption | Very Low | High |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent | Fair (when wet) |
| Suited Climate | Humid / Wet | Dry / Controlled |
This stability makes Valox a reliable material for applications where consistency is key.

The core issue with Nylon 66 in damp environments is its susceptibility to hydrolysis, where water molecules break down the polymer chains. This process degrades the material’s mechanical and electrical integrity over time. For parts like automotive connectors exposed to the elements, this can lead to premature failure.
Technical Breakdown: PBT vs. PA66
Valox, a type of PBT, has a chemical structure that is inherently more resistant to water. Its lower moisture absorption means that its physical dimensions and electrical properties remain remarkably stable, even when subjected to high humidity. This is a critical advantage for maintaining tight tolerances in connector designs. The material’s Crystallinity6 also contributes to this, creating a more compact structure that resists water ingress.
Impact on Electrical Performance
Moisture absorption directly impacts a material’s insulating capabilities. When Nylon 66 absorbs water, its dielectric strength and volume resistivity can decrease significantly. Based on our tests with clients, this shift can compromise the safety and reliability of an electrical component. Valox maintains its excellent electrical properties far more consistently.
| Electrical Property | Valox (PBT) in Humid Air | Nylon 66 (PA66) in Humid Air |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | Stable | Decreases |
| Volume Resistivity | Stable | Decreases |
| Dimensional Change | Minimal | Significant |
At MTM, we often guide clients toward Valox for mold trials involving parts destined for humid regions, ensuring their designs pass validation without moisture-related setbacks.
For electrical applications in humid environments, Valox’s low moisture absorption provides superior dimensional and electrical stability. Nylon 66 is a strong material but is compromised by water, making Valox the more reliable choice for components requiring long-term performance consistency.
Design Guidelines For Valox: Ribs, Bosses, And Wall Thickness
When designing parts with Valox, managing wall thickness is your first line of defense against defects. Uniform thickness is ideal, but when variations are necessary, the transition should be gradual. Abrupt changes can cause stress concentrations and sink marks, especially with fast-cycling materials like PBT.
Optimal Wall Thickness
Maintaining the correct wall thickness ensures that the Valox material flows evenly and cools uniformly. This prevents warping and sink marks, which are common issues. Based on our tests, sticking to recommended ranges is critical for part quality and performance.
General Valox Thickness Ranges
| Valox Grade Type | Recommended Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|
| Unfilled Grades | 1.0 – 3.5 |
| Glass-Filled | 1.5 – 5.0 |
| Flame Retardant | 1.2 – 4.0 |
Rib Design Fundamentals
Ribs add strength without adding significant thickness or weight. However, poorly designed ribs can create cosmetic problems like sink marks. The key is to make the rib’s base thickness a fraction of the adjacent wall’s thickness, usually around 50-60%. This minimizes material accumulation.
Proper Valox part design is more than just theory; it directly impacts production efficiency and final part quality. The semi-crystalline nature of PBT means it shrinks as it cools, and thick sections are the primary cause of unsightly sink marks on the opposite surface.
Preventing Common Defects
To avoid these issues, the ratio of rib thickness to wall thickness is non-negotiable. I always advise clients to start at 50% and only increase if structural analysis demands it. A generous radius at the base of the rib also helps the Melt Flow Index7 and reduces stress.
Rib Design Best Practices
| Parameter | Recommendation | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Rib Height | < 3x Wall Thickness | Prevents cooling issues and breakage. |
| Rib Base Radius | > 0.5x Wall Thickness | Reduces stress concentration. |
| Rib Spacing | > 2x Wall Thickness | Ensures adequate cooling between ribs. |
| Draft Angle | 0.5° – 1.5° per side | Facilitates easy part ejection. |
At MTM, we ensure you have the correct Valox grade for your mold trial. This allows you to test these design principles with the exact material intended for production, saving you from costly tool modifications later on. A successful trial validates both the mold and the part design.
Adhering to Valox-specific guidelines for wall thickness and rib-to-wall ratios is essential. These rules prevent common molding defects like sink marks, ensuring the structural integrity and aesthetic quality of your final PBT components. This proactive approach saves time and reduces costs.
Gate Placement Strategies For Glass-Reinforced Valox Parts
When molding with glass-reinforced Valox, gate placement is a critical decision. It directly influences how the glass fibers align within the polymer melt. This alignment, or fiber orientation, dictates the part’s final strength and can cause warpage if not managed correctly. Proper gate design for PBT is essential.
The Challenge of Fiber Orientation
Incorrect gating causes fibers to align in ways that create internal stress. This often leads to parts warping after ejection. The goal is to create a predictable and uniform flow front, ensuring fibers are oriented to reinforce the part where it needs strength most.
Weld Lines and Aesthetics
Weld lines form where two melt fronts meet. In glass-filled Valox, fibers fail to intermingle across this line, creating a weak point and a visible surface blemish. The gate location determines where these weld lines appear on the final part.
| Gate Location | Impact on Fiber Orientation | Impact on Weld Lines |
|---|---|---|
| End of Part | Aligns fibers along the flow path | Pushes weld line to the part’s end |
| Center of Part | Creates a radial fiber pattern | Can create multiple weld lines at edges |
| Near Critical Area | Can reinforce specific features | May place a weld line in a weak spot |

The physics behind these issues is straightforward but critical. Glass fibers act like tiny steel bars in concrete; they only provide strength along their length. When the Valox resin flows into the mold, these fibers align with the direction of flow, much like logs in a river. This directional alignment is the root cause of many challenges.
Understanding Warpage from Fiber Orientation
The primary issue is Anisotropic Shrinkage8. The material shrinks less in the direction of fiber orientation and more in the transverse (cross-flow) direction. This differential shrinkage creates internal stresses that bend or twist the part as it cools. A poor gate design PBT exacerbates this effect.
Strengthening Weak Weld Lines
Weld line strength is a major concern. Because fibers do not cross the weld line, these areas can be significantly weaker than the rest of the part. In our tests with clients, we’ve found that a well-placed gate can move a weld line to a non-critical area, preserving the part’s structural integrity.
| Problem | Gate Strategy Solution | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Warpage | Gate along the longest axis | Promotes uniform, unidirectional flow |
| Weak Weld Line | Position gate to move the weld line | Places the weak point in a low-stress area |
| Surface Blemish | Use a fan or tab gate | Reduces shear and improves surface finish |
At MTM, we often help clients analyze their gate design. Sometimes, a simple adjustment can prevent costly tool modifications. It’s about controlling the flow front of the Valox resin from the very start.
Proper gate placement for glass-reinforced Valox is not just a suggestion; it’s a requirement. It governs fiber orientation and weld line location, directly impacting the part’s mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and appearance. Strategic gate design is essential for successful molding outcomes.
Controlling Mold Shrinkage And Warpage In Valox PBT
Controlling shrinkage and warpage in Valox PBT is a common challenge. Success depends on mastering key processing parameters. These adjustments directly influence the final part’s dimensional stability, preventing costly injection molding defects.
Key Processing Parameters
Fine-tuning your process is crucial. The interaction between cooling and packing determines the outcome. Small changes here can have a significant impact on part quality.
Cooling Time’s Role
Sufficient cooling time allows the crystalline structure to set properly. Rushing this step often leads to unpredictable shrinkage as the part cools outside the mold. This can cause severe warpage.
Packing Pressure’s Impact
Packing pressure compensates for material shrinkage as it cools. Proper application ensures the cavity is completely filled, reducing voids and sink marks.
| Parameter | Effect on Shrinkage | Effect on Warpage |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Packing Pressure | Decreases | Can Increase (if uneven) |
| Increased Cooling Time | Stabilizes | Decreases (if uniform) |
| Decreased Melt Temp | Increases | Can Increase |
| Increased Mold Temp | Decreases | Can Decrease (if uniform) |

As a semi-crystalline material, Valox PBT’s behavior during cooling is distinct. The polymer chains organize into ordered structures, which causes a significant volume reduction. This process is the primary driver of the high Valox shrinkage rate.
Troubleshooting for Engineers
When facing defects, focus on the relationship between pressure and time. The goal is to manage the material’s transition from a molten to a solid state inside the mold.
The Problem with Insufficient Packing
If packing pressure is too low or applied for too short a duration, the material will pull away from the mold walls as it crystallizes. This leads to higher-than-expected Volumetric Shrinkage9 and can result in sink marks or voids. It’s a frequent cause of failed parts.
Balancing Parameters for Reduced Warpage PBT
Achieving reduced warpage in PBT parts requires a balanced approach. While high packing pressure reduces shrinkage, if applied unevenly, it can create internal stresses that cause warpage later. We often advise clients to start with a moderate pressure and adjust based on part geometry.
| Scenario | Symptom | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low Packing Pressure | Sink marks, high shrinkage | Increase packing pressure or duration |
| High Packing Pressure | Flash, high internal stress | Decrease packing pressure, check clamp tonnage |
| Short Cooling Time | Warpage after ejection | Increase cooling time, ensure uniform cooling |
Having a consistent supply of Valox from a reliable source like MTM is critical. It allows you to develop a stable process without worrying about material variations affecting your results.
Effectively managing Valox PBT requires balancing cooling time and packing pressure. This control is fundamental to preventing common injection molding defects and ensuring parts meet precise dimensional specifications.
Screw Design And Injection Speed Considerations For PBT
Processing PBT requires careful attention to screw design and injection speed to achieve optimal results. Based on our tests, a general-purpose screw is typically sufficient, but the specifics matter. For materials like Valox, a proper setup prevents degradation and ensures part integrity.
Recommended Screw Parameters
A screw with a length-to-diameter (L/D) ratio between 20:1 and 24:1 is ideal. This provides adequate residence time for uniform melting without risking thermal degradation. The compression ratio should be kept moderate.
| Parameter | Recommended Value | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| L/D Ratio | 20:1 – 24:1 | Ensures uniform melting |
| Compression Ratio | 2.5:1 – 3.0:1 | Prevents excessive shear heat |
| Screw Type | General Purpose | Sufficient for most PBT grades |
A Note on Nozzles
Always use a free-flow nozzle. Avoid shut-off nozzles as the shear they introduce can easily degrade PBT, leading to brittle parts. This small detail can make a significant difference in final part quality.

Injection speed is a critical balancing act when molding PBT. Its low melt viscosity means it flows easily, but this characteristic also makes it susceptible to issues if the speed is not managed correctly. You must find the sweet spot between filling the part and damaging the material.
Avoiding Shear Burning
High injection speeds generate significant friction, or shear stress, within the polymer chains. This can cause the material to burn, leaving dark streaks on the part. When we work with clients on their Valox trials, we always advise starting with a moderate speed and increasing it cautiously.
Filling Thin-Walled Sections
Conversely, an injection speed that is too slow can lead to premature freezing, resulting in short shots, especially in thin-walled sections. For complex geometries, a multi-stage injection profile is often necessary to fill the part completely without causing shear burning. The key is to use a higher speed for thin sections and slow down for thicker areas. A high Shear rate10 can quickly degrade the material if not managed.
| Injection Stage | Speed | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Fill | Moderate | Fills runners and gate area smoothly |
| Main Fill | Fast | Fills thin-walled sections quickly |
| Pack/Hold | Slow | Packs out thick sections, reduces sinks |
At MTM, we help clients troubleshoot these issues by ensuring they have the right material and the foundational processing knowledge for a successful trial.
In summary, successful PBT molding relies on a well-chosen screw and a balanced injection speed. A proper L/D ratio prevents material degradation, while carefully controlled injection velocity ensures complete filling without causing shear-induced defects.
Automotive Connector Applications: Why Valox Remains The Standard
When selecting an automotive connector resin, the under-hood environment presents the toughest challenge. Valox PBT has become the standard not by chance, but by consistently delivering performance where it matters most. It reliably withstands extreme temperatures, vibrations, and chemical exposure common in engine compartments.
Key Performance Requirements
For engineers, material choice is critical. Failure is not an option when it comes to vehicle safety and reliability. Valox offers a balanced profile that meets these strict demands, ensuring connectors maintain their integrity over the vehicle’s lifespan. Below is a simplified comparison.
| Property | Requirement | Valox Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Withstand -40°C to 150°C | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Resist oils, fuels, grease | High |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength | Excellent |
| Dimensional Stability | Low moisture absorption | High |
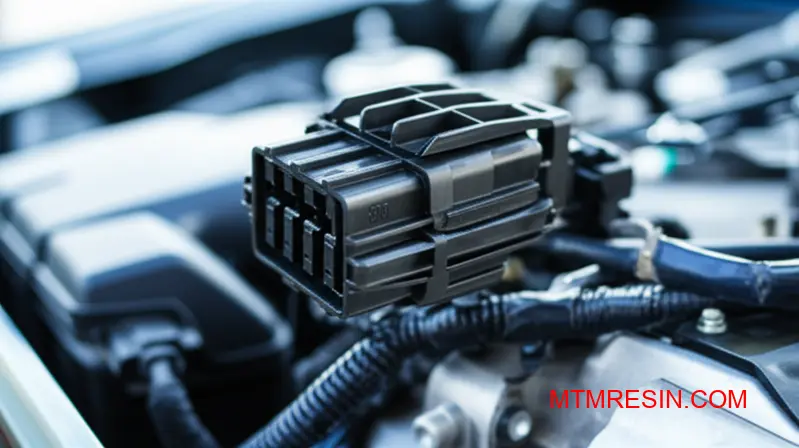

The real test for under-hood PBT applications is long-term exposure to harsh conditions. It’s not just about surviving a single event, but about enduring years of service. Valox grades are specifically formulated for superior automotive chemical resistance against fluids that would degrade lesser materials.
Resisting Automotive Fluids
Connectors are frequently exposed to motor oil, gasoline, brake fluid, and coolant. These chemicals can cause materials to swell, soften, or crack. Valox PBT maintains its structural and electrical properties, preventing premature failure. This resilience reduces the risk of costly warranty claims and ensures system reliability.
Surviving Thermal Cycling
An engine compartment experiences constant temperature swings, from freezing cold starts to high operating heat. This thermal cycling can cause materials to expand and contract, leading to micro-cracks and connection failures. Valox shows minimal dimensional change, a key factor in preventing issues like Chemical Stress Cracking11 when combined with mechanical and chemical loads.
| Fluid Exposure | Valox Resistance | Impact on Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Oil / Grease | Excellent | No swelling or loss of integrity |
| Gasoline / Diesel | Very Good | Maintains seal and connection force |
| Brake Fluid | Excellent | Prevents material degradation |
| Coolants (Glycol) | Very Good | Stable performance over time |
At MTM, we often supply specific Valox grades to clients for mold trials in China, ensuring their parts meet these demanding under-hood requirements from the start.
Valox PBT’s blend of thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional integrity makes it the benchmark for under-hood connectors. Its proven performance in these demanding environments ensures the long-term reliability required in modern automotive applications, preventing costly failures down the line.
Boost Your Project Success: Choose MTM for Valox PBT
Ready for seamless Valox PBT sourcing and mold trials in China? Contact MTM now for instant access to in-stock engineering-grade Valox and expert guidance—no overseas shipping or delays. Get a fast quote, accelerate your precision engineering, and ensure material consistency with MTM’s trusted local support!

-
Understand how this chemical process can impact material integrity and part performance during high-temperature processing. ↩
-
Learn how this property impacts long-term part performance under constant load, crucial for structural component design. ↩
-
Understanding this property helps in designing safer and more reliable high-voltage electrical components. ↩
-
Understanding this property helps predict a material’s resistance to bending under load. ↩
-
Understand how this index quantifies material flammability, aiding in advanced material selection for critical applications. ↩
-
Learn how a material’s internal structure dictates its real-world performance and moisture resistance. ↩
-
Understanding this property helps predict material behavior during molding, improving design accuracy and process control. ↩
-
Learn how this property causes warpage and affects the dimensional accuracy of molded parts. ↩
-
Understanding this concept helps predict material behavior and improve part quality beyond simple linear measurements. ↩
-
Understanding this concept is key to optimizing material flow and preventing molecular degradation during the injection process. ↩
-
Understanding this failure mechanism is crucial for designing durable plastic parts exposed to common automotive chemicals. ↩
